






DNS servers or Domain Name Server is responsible for converting URLs and domain names into IP addresses so that computers can understand and use them. On the other hand, we have FTP or File Transfer Protocol which is a standard network protocol used for transferring files from one host to another over a TCP-based network. We will present this tutorial to give a full explanation of DNS and FTP and also find out which one is the backbone of your website’s functionality.
It is very important to know the concept of DNS and its functionality. If a user tries to enter a website from a personal computer, laptop, or tablet using the internet, the user should use DNS. So, understanding the usage of DNS is very important:
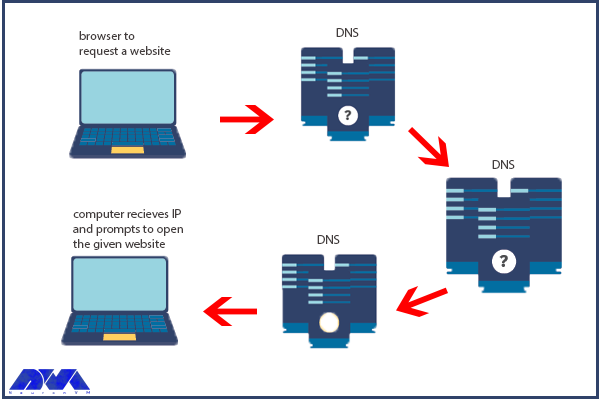
Browsers and other Internet activities rely on DNS to provide the information needed to connect users to remote hosts as quickly as possible. DNS mapping is distributed across the Internet in a chain of authorities. ISPs, access companies, as well as governments, universities, and other organizations typically have dedicated ranges of IP addresses and an assigned domain name. They also run DNS servers to manage the mapping of those names to those addresses. Most URLs are built around the domain name of the web server responsible for receiving client requests. Before we start and deal with the main issue, we recommend you use the cheap dedicated server plans of our website to setup DNS.
DNS is a critical component of website functionality. Without DNS, users would have to remember the IP address of every website they want to visit, which would be impractical. DNS allows users to access websites using user-friendly domain names, making it easier to navigate the internet. In addition, DNS helps to distribute traffic to different servers, ensuring that the load is evenly balanced and the website remains accessible even under heavy traffic.
Configuring DNS can be a complex process, but most web hosting providers offer tools and guides to make it easier. The first step is to choose a DNS provider. It can be either your web hosting provider or a third-party provider like Cloudflare or Google DNS. Once you’ve chosen a provider, you’ll need to set up your DNS records. These records include information about your domain name, IP address, and other settings. This process can vary depending on your web hosting provider and the type of DNS records you need to setup.
One common issue with DNS configuration is DNS propagation, which refers to the time it takes for DNS changes to take effect. This can be frustrating for website owners who need to make changes quickly. Note that it’s important to be patient and allow time for the changes to propagate. Another common issue is DNS caching, which can cause outdated information to be displayed. Clearing your DNS cache can help resolve this issue.
Even with proper configuration, DNS issues can still occur. One common issue is DNS resolution failure, which occurs when a DNS server is unable to resolve a domain name. The reason may be a variety of factors, including incorrect DNS records, network connectivity issues, or DNS server errors. To troubleshoot this issue, start by checking your DNS records to ensure they are correct. You can also try using a different DNS server or contacting your web hosting provider for assistance.
Another common issue is DNS hijacking. This problem occurs when a malicious actor redirects traffic from a legitimate website to a fake website. This can be difficult to detect, but there are tools available to help identify and prevent DNS hijacking. It’s also important to keep your DNS records secure and to use strong passwords to prevent unauthorized access.
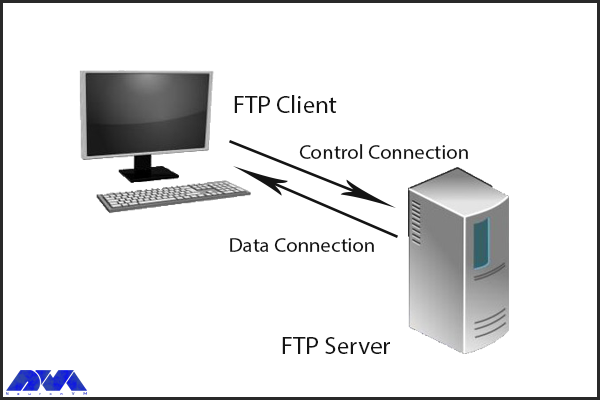
FTP, or File Transfer Protocol, is another critical component of website functionality. It is used to transfer files between computers and servers, allowing website owners to upload and manage their website files. FTP works by using a client-server model, where the client (usually a web developer or website owner) connects to the server using a username and password and then transfers files between the two computers. The importance of FTP in website functionality cannot be overstated. Without FTP, website owners would need to manually upload and manage their website files, which would be a time-consuming and error-prone process. FTP also allows website owners to easily make changes to their website files, ensuring that their website stays up-to-date and secure.
FTP is an essential component of website functionality, as it allows website owners to upload and update content on websites. Without FTP, website owners would need to manually upload files to their servers, which would be time-consuming and prone to errors. FTP makes it easy to update content and ensure that the website is always up-to-date.
Configuring FTP is typically done through a web hosting control panel or FTP client software. The first step is to create an FTP account, which includes a username and password that the client will use to connect to the server. Once the account is created, the client can then connect to the server using an FTP client like FileZilla or Cyberduck. From there, they can transfer files between their computer and the server.
One common issue with FTP configuration is connection errors, which can be caused by incorrect login credentials or firewall settings. To troubleshoot this issue, double-check your login credentials and ensure that your firewall is not blocking FTP traffic. Another common issue is file transfer errors. It can be caused by file permissions or file size limits. To troubleshoot this issue, ensure that your file permissions are properly configured and your FTP client is set up to handle large file transfers.
Even with proper configuration, FTP issues can still occur. One common issue is FTP connection timeouts, which occur when the client is unable to connect to the server. This can be caused by network connectivity issues or server errors. To troubleshoot this issue, try connecting to the server from a different network or contacting your web hosting provider for assistance.
Another common issue is FTP data transfer errors, which occur when files are transferred incompletely or with errors. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including file size limits, file permissions, or network connectivity issues. To troubleshoot this issue, ensure that your file permissions are properly configured and that your FTP client is set up to handle large file transfers.
Both DNS and FTP are critical components of website functionality, but they serve different purposes. DNS is responsible for translating domain names into IP addresses, allowing users to access websites using human-readable names. FTP, on the other hand, is used to transfer files between computers and servers, allowing website owners to upload and manage their website files.
While both DNS and FTP are important, DNS is arguably the more critical component. Without DNS, users would be unable to access your website, regardless of how well it’s configured. FTP, on the other hand, is important for website management but does not directly impact user experience. That being said, both DNS and FTP are essential to ensuring that your website runs smoothly and efficiently.
In conclusion, DNS and FTP are both critical components of website functionality. DNS is responsible for translating domain names into IP addresses. While FTP is used to transfer files between your computer and your website’s server. Both are essential for ensuring that your website runs smoothly and remains accessible to users. While configuring DNS and FTP can be a complex process, website owners need to understand how they work and how to troubleshoot common issues. Whether you’re a seasoned webmaster or a newbie to the world of website management, understanding DNS and FTP is essential for the success of your website.
It turns domain names into IP addresses and allows browsers to find websites and other resources.
FTP client and internet connection are needed for using FTP. Aso you will need to know the FTP server’s IP addresses or hostname.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 4 / 5. Vote count: 1
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
 Tags
Tags

If you decide to recover your data through Jetbackup, which has become very popular, and your contro...



 Tags
Tags
In today's digital era, Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) has become an essential tool for business...



 Tags
Tags
What is your opinion about this Blog?








